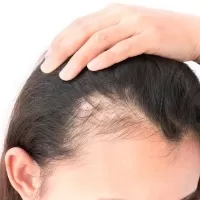
Menopause and perimenopause can have a significant impact on hair, with many women experiencing thinning, hair loss, or changes in texture. These changes are largely due to hormonal fluctuations, particularly the decrease in oestrogen and progesterone levels, which can affect the hair growth cycle. Oestrogen normally helps keep hair in the growth phase, so as levels decline, hair may enter the shedding phase more quickly, leading to thinning or noticeable hair loss. Additionally, the relative increase in androgens (male hormones) can lead to more pronounced hair thinning on the scalp or increased facial hair growth.
Hair
Managing hair changes during menopause may involve adopting a hair care routine tailored to thinning hair, using gentle shampoos and conditioners, considering hormonal treatments or supplements, and consulting with a healthcare provider.